Injured?
This simple word can have a major impact on professional & recreational athletes. Luckily, as an athlete you know longer
have to be susceptible to injuries and long downtime: microcurrent therapy is an effective option for immediate post injury
treatment, physical maintenance, and shortening recovery time.
Recovery
When you are a professional or recreational athlete, it is inevitable that at some point in your competitive career you will be injured.
For the best recovery, it is recommended to use microcurrent in conjunction with traditional treatment methods. When injured, treatment sessions are more aggressive, meaning you should treat more frequently and for longer duration.
Why the AMS 200?
The AMS 200 is a portable unit that you can easily store, keep it in your sports bag, and use immediately after you have an injury. The AMS 200 can attach to standard adhesive electrodes or various conductive cloth garments to treat all different body parts that may become injured.
Professional Athletes & Microcurrent
Microcurrent has been used since the 1980s to help professional and college athletes get
back in the game after an injury. In 1986, the University of Texas Women’s Track and Field
team became the first major university athletic program to use microcurrent stimulation
therapy. That same year, in preparation for the 1986 season the NFL Player’s Association
began studying the use of microcurrent therapy for treating and rehabilitating athletes who
had traumatic and chronic injuries.
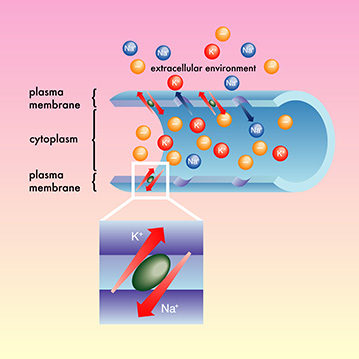
The Cellular Physiology of Tissue Self-Repair & Micro-Current Technology
Studies have revealed that microcurrent therapy helps in restoring metabolic processes
that are responsible for healing. It regulates the energy levels of the body by promoting
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) production, which is the major energy fuel for all the
biochemical reactions. As the energy level increases, the body's ability to remove
metabolic wastes via active transport is enhanced, hence preventing accumulation of toxic
substances. The same process takes place in injured cells, which in turn, enhances
distribution, blood circulation and removal of wastes. This way, new healthy cells replace
the injured ones. The body after receiving microcurrent therapy also stimulates protein
synthesis, ion exchange and maintains neuromuscular systems. In such a condition, the
body restores its enzymatic activities and their corresponding metabolic processes.
Microcurrent therapy also promotes the glycogen utilization by the muscle cells. Overall,
the normal functioning of the body's cells and tissues are restored. Micro-current therapy
is more effective than other electrotherapy procedures. In this technique, the current is so
small that there is no tissue resistance, which is observed in case of electrotherapy.
Consequently, the patient rarely feels the current while undergoing the treatment.